
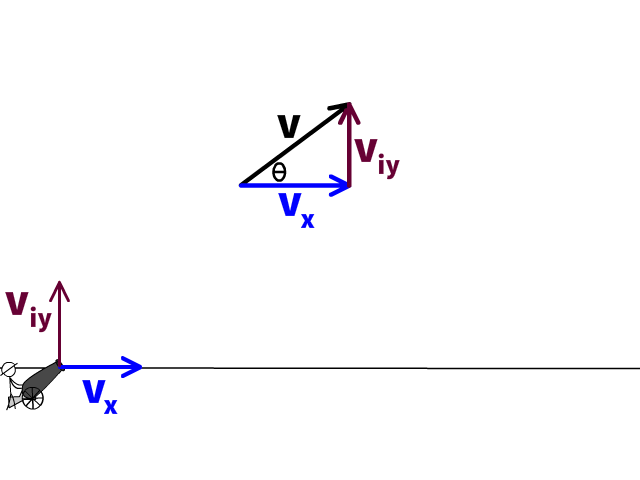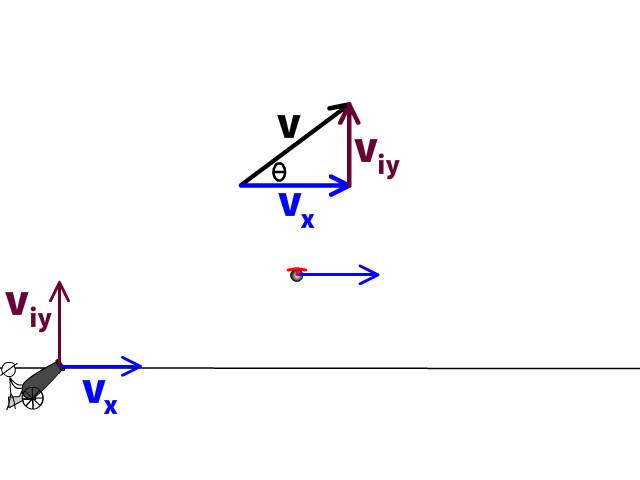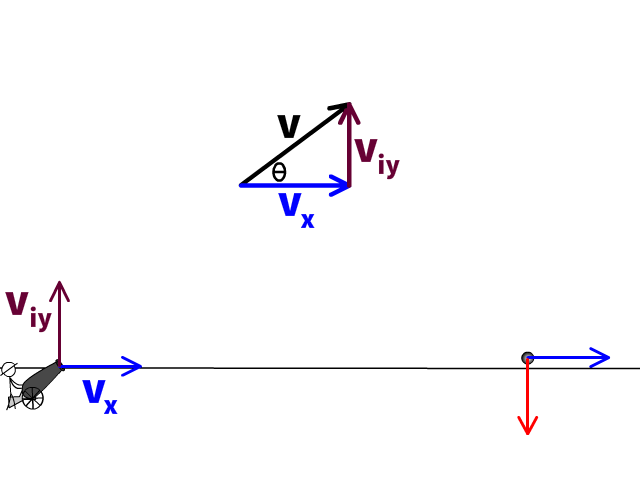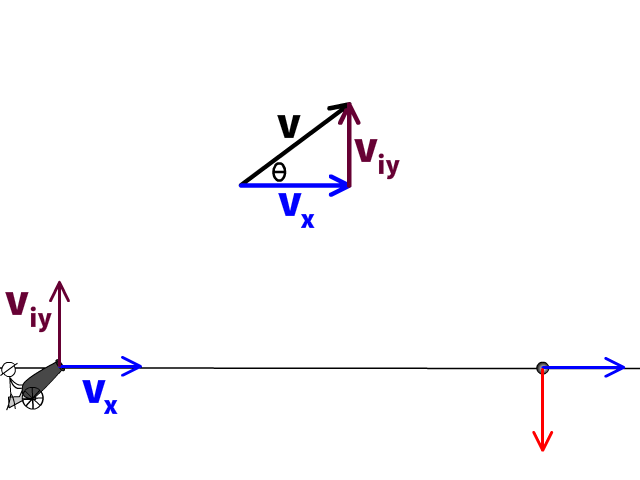
If not, please take advantage of the additional practice found in the companion text. If you have mastered the concepts, you should find that the questions in the scenarios can be easily answered. PA Homeschooler PHYSICS 1 Students ONLY: Prior to moving to the next assignment in the workflow, you must work through the following scenarios in the AP Physics 1 Student Workbook. Assume that the atmospheric density decreases with elevation. Additionally, use your ideas to predict if a projectile with an extremely big max height (very large initial speed) would have a larger range if shot at 45° or at 50°. Describe what you think the effect of air resistance would be on the range of a projectile. (moderate) In every projectile example thus far, we have assumed free-fall conditions (no air resistance). Use your algebraic skills to treat the term tanθ as the unknown in a quadratic equation.ġ0. Clue: It might be useful for you to remember the trig identity, 1/(cos 2θ) = 1 + tan 2θ, as a way to simplify your analysis. Determine the minimum and the maximum kicking angles which will result in a field goal. The goal post crossbar is 3.44 m above the ground. The kick begins 40.0 m in front of the goal posts. (moderate) A kicker on the football team gives the ball an initial velocity of 22.0 m/s. Matt Ryan throws a football to Julio Jones who catches it at the same height. The video here talks out the logic to determine givens and solve. The other projectile follows the red trajectory. Get practice trying additional angular projectile motion problems and check your solutions with our help in the video here. The projectile fired at the lower angle bounces (upon hitting the ground) losing some of its energy while following the black trajectories. (OPTIONAL hard) Two objects are launched from the same position, with the same initial speeds, but at different angles. Find the initial velocity, the maximum height and the overall velocity at maximum height.Ĩ. 1.6 seconds after release, the rock reaches its maximum height. (moderate) A rock is tossed at a 42°angle at an initial height of 1.2 m from the ground. If the net is 12.0 m from the ball (in the x-direction), and the net height is 0.90 m, by how much does the ball clear the net?ħ. The ball is 2.37 m above the ground when struck by the racquet. (moderate) A tennis player hits a ball with an initial speed of 23.6 m/s perfectly horizontally. Figure 4.12 (a) We analyze two-dimensional projectile motion by breaking it into two independent one-dimensional motions along the vertical and horizontal axes. My main objectives were: (1) To discuss projectile motion as a combination of a uniform horizontal motion and a uniformly decelerated/accelerated vertical motion. Find the initial speed and the maximum height.Ħ.

It lands on the ground 9400 m (in the x-direction) from the base of the launch site. (moderate) A projectile is launched at a 35° angle from a height of 3300 m off the ground. Assume that the ball is hit 1.0 m above the ground initially. Find.Ĭ) The velocity components and the speed of the ball when it reaches the wall.ĥ. (moderate) A home run is hit in such a way as the baseball just clears a wall (21.0 m tall) located 130.0 m from home plate. Additionally, if one assumes that the initial speed remained the same for all firing angles, what is the maximum range for the cannonball?Ĥ. Determine the time it takes for the cannonball to hit the ground and the distance from the base of the wall where the projectile lands. (moderate) A cannonball (placed on a wall 20 m above the ground) is shot at 20° firing angle with a initial speed of 17 m/s. Projectile D: Firing angle = 60°, initial speed = 40 m/sģ. Projectile C: Firing angle = 15°, initial speed = 40 m/s Projectile B: Firing angle = 45°, initial speed = 40 m/s Projectile A: Firing angle = 30°, initial speed = 40 m/s (easy) Rank the range of the following projectiles: Does this athlete have a greater overall speed at takeoff or on landing? Explain your response.Ģ. Compare and contrast the four trajectories shown.ī) If the water spouts in the picture below shot the water at a slightly higher angle, would the landing place be closer to or further from the spouts? Assume Δy = 0.Ĭ) Analyze the snowboarder from the 2018 winter Olympics in PyeongChang. This physics product contains everything you need to teach projectile motion. (easy) a) Study the image below from the 2016 Rio Olympics. Now to find the total time in the air, we use the definition of acceleration to find the time it takes the ball to get to the top of its arc, the acceleration in this case being $g = 9.8 m/s^2.$ We can rearrange that definition to find the elapsed time.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
